Tel: 650-980-4870
Blog
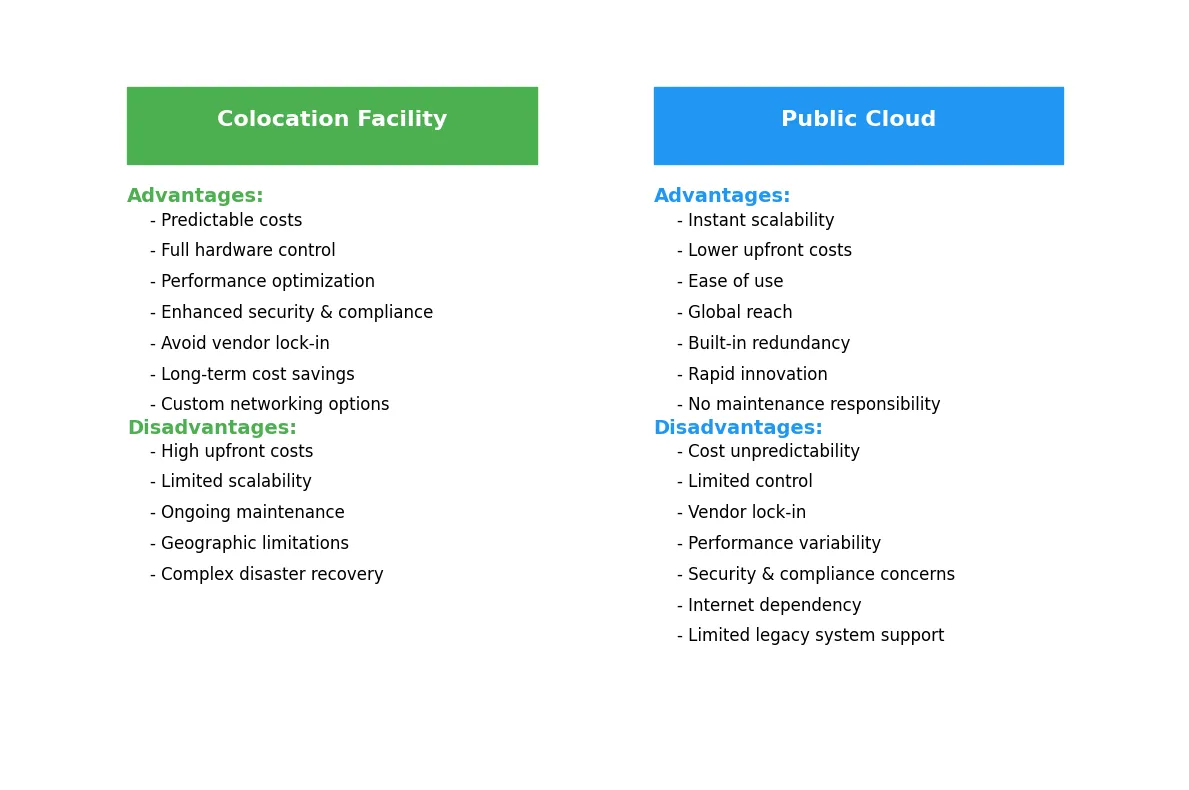
Colo vs. Public Cloud
Here’s a balanced comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of using a colocation facility versus a public cloud:
Colocation Facility
Advantages
Cost Predictability
Colocation involves fixed costs for space, power, cooling, and network connectivity, making budgeting more predictable compared to the variable costs of public cloud services.
Full Hardware Control
You own and manage your hardware, allowing for complete control over configurations, performance, and security.
Performance Optimization
Custom hardware tailored to your workloads can deliver better performance, especially for latency-sensitive or resource-intensive applications.
Data Security and Compliance
Physical control over your servers can help meet strict compliance requirements (e.g., HIPAA, PCI-DSS) and provide enhanced data security.
Avoiding Vendor Lock-In
You are not tied to a specific cloud provider, giving you flexibility in choosing software, hardware, and services.
Long-Term Cost Savings
For consistent workloads, colocation can be more cost-effective over time compared to the pay-as-you-go model of public cloud services.
Custom Networking
Colocation facilities allow for custom networking setups, such as private networks or direct connections to other data centers.
Support for Legacy Systems
Colocation is ideal for organizations that rely on legacy systems or specialized hardware that cannot easily migrate to the cloud.
Disadvantages
High Upfront Costs
You must purchase and maintain your own hardware, which requires significant initial investment.
Limited Scalability
Scaling requires purchasing and installing additional hardware, which can be slower and less flexible than the instant scalability of the cloud.
Ongoing Maintenance
You are responsible for maintaining and upgrading your hardware, which requires skilled personnel and additional resources.
Geographic Limitations
While you can choose the location of your colocation facility, expanding to new regions requires additional contracts and hardware deployments.
Disaster Recovery Complexity
Setting up disaster recovery and redundancy requires careful planning and additional costs, unlike the built-in redundancy of public cloud providers.
Public Cloud
Advantages
Scalability and Flexibility
Public cloud services allow you to scale resources up or down instantly, making them ideal for dynamic or unpredictable workloads.
Lower Upfront Costs
There is no need to purchase hardware; you pay only for the resources you use, reducing initial capital expenses.
Ease of Use
Cloud platforms offer user-friendly interfaces, APIs, and managed services, reducing the need for in-house expertise.
Global Reach
Public cloud providers have data centers worldwide, enabling you to deploy applications closer to your users with minimal effort.
Built-In Redundancy and Disaster Recovery
Public cloud providers offer high availability, redundancy, and disaster recovery options as part of their services.
Rapid Innovation
Cloud providers frequently release new features, tools, and services, allowing you to adopt cutting-edge technologies quickly.
No Maintenance Responsibility
The cloud provider handles hardware maintenance, upgrades, and replacements, freeing your team to focus on other priorities.
Disadvantages
Cost Unpredictability
Costs can quickly escalate with increased usage, data transfer, or unexpected scaling, making budgeting more challenging.
Limited Control
You have no control over the underlying hardware or infrastructure, which may limit customization and optimization.
Vendor Lock-In
Relying on a single cloud provider can make it difficult and costly to migrate to another platform or adopt a multi-cloud strategy.
Performance Variability
Shared infrastructure can lead to performance variability, especially during peak usage periods.
Data Security and Compliance Concerns
While cloud providers offer robust security, some industries may require physical control over data, which is not possible in the public cloud.
Dependency on Internet Connectivity
Public cloud services rely on internet access, and outages or latency issues can disrupt operations.
Limited Support for Legacy Systems
Legacy applications or specialized hardware may not be compatible with cloud environments, requiring significant reengineering.
Summary
Colocation is ideal for organizations that need full control over their hardware, predictable costs, and support for legacy systems, but it requires significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance.
Public Cloud is best for businesses that prioritize scalability, flexibility, and ease of use, but it can lead to cost unpredictability and limited control over infrastructure.
The choice between colocation and public cloud depends on your organization's specific needs, including workload predictability, compliance requirements, budget, and technical expertise. Many organizations adopt a hybrid approach, combining the benefits of both.
Menu
Services
© Copyright 2023. Optimal Outcomes. All rights reserved.
